The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) is on the horizon, and it’s time for AI business and tech leaders to pay close attention.
The recent passage of the AI Act by the European Parliament on June 14th marks a significant step towards regulating AI technologies within the EU. Now the Parliament, Commission, and Council will engage in a final process to shape the law, with implementation expected in 2024.
Let’s explore the key elements of the AI Act and understand what they mean for AI practitioners and organizations:
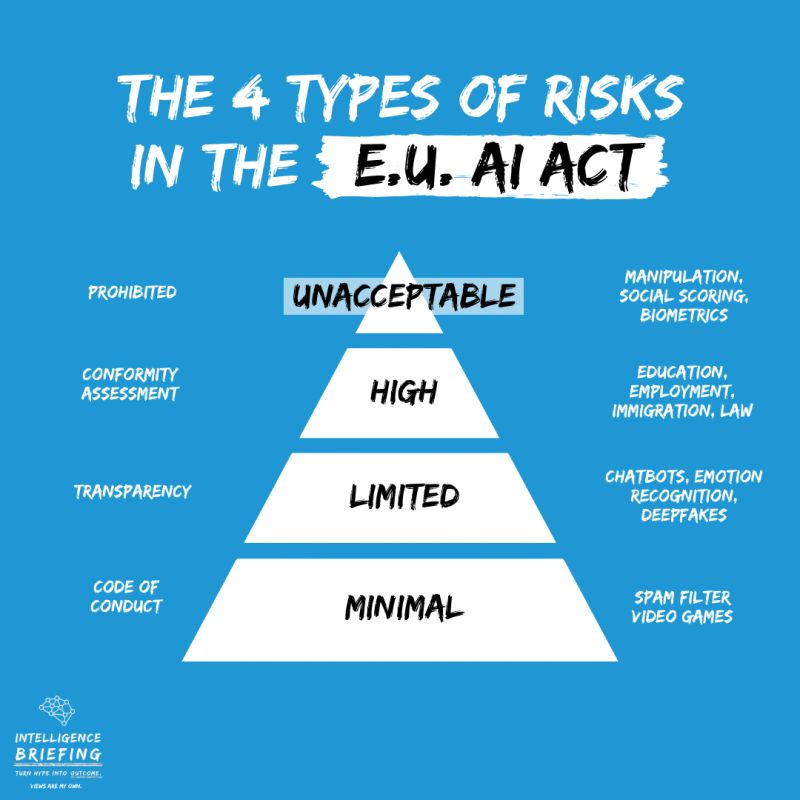
1. Standardized Documentation for Use Cases and Risk Levels:
The AI Act classifies specific use cases into four risk categories: unacceptable, high, medium, and low risk. By focusing on use cases rather than ML models, the law aims to identify and manage potential risks associated with AI applications. For instance, the AI Act prohibits high-risk uses like ‘social score’ systems to protect individuals from potential harm.
2. Documentation Accessibility and Stakeholder Engagement:
The AI Act expands the scope of stakeholders involved in AI Governance, requiring a shift in how AI systems and use cases are documented. Organizations must bridge the gap between technical intricacies and business-level concepts to provide comprehensive understanding. Effective documentation solutions will enable transparency, compliance, and informed decision-making.
3. Generative AI Liability and Risk Mitigation:
The EU Parliament introduces clearer requirements for organizations deploying foundational models and generative AI systems. While the exact requirements are still evolving, preparing for risk mitigation is essential. Conducting internal studies to assess the limitations of generative AI and documenting results can be a proactive step towards compliance with the AI Act.
4. Testing & Human Evaluations for Real-World Performance:
Evaluation metrics based on training data alone may not reflect real-world performance. Organizations should develop their own evaluation tasks and testing suites to ensure model quality and performance. Human evaluations play a crucial role in assessing AI systems’ effectiveness, fairness, and impact.
5. Model Update Workflows and Compliance:
High-risk AI use cases require structured processes for model updates. Different changes to ML models may trigger varying levels of review for compliance purposes. Establishing clear workflows for model updates ensures ongoing compliance with the evolving regulatory landscape.
While the final version of EU’s AI Act is still taking shape, it is likely that we will see similar AI regulation in the US and other countries very soon.
It is critical for AI teams to proactively prepare for the forthcoming regulatory requirements. By embracing transparency, accountability, and risk mitigation strategies, we can navigate the evolving AI landscape effectively.
What are your thoughts on EU’s proposed AI regulation?